Protocol Watch
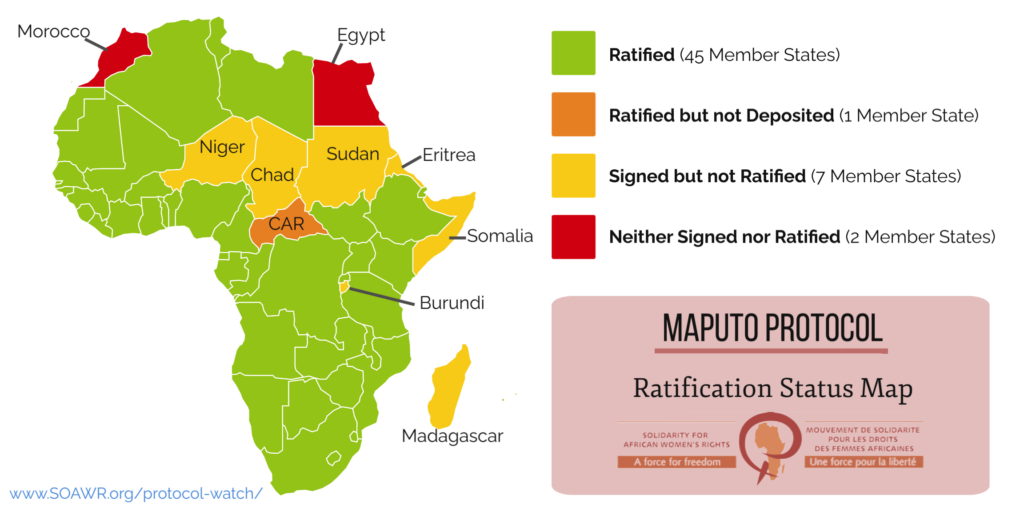
The position as of 1st of December, 2023
Not Signed
Signed but not Ratified
Ratified
Please note that the Central African Republic (CAR) ratified the Maputo Protocol on the 10th of May 2012 but is yet to deposit the original instrument of ratification to the African Union Commission.
What is ratification?
Ratification is formal act of a State through which it establishes at the international level its consent to be bound by a treaty it has signed. At the national level it refers to an act prescribed within the law or constitution which a state takes to express intention and consent to be bound by an international instrument. Likewise, ‘accession’ is the formal act of a State accepting to become a Party to a treaty and to be bound by it.
Article 28 of the Maputo Protocol provides for countries to sign, ratify or accede to the Protocol in accordance with their constitutional procedures. The laws of a country determine how a treaty is to be ratified or acceded to by the executive or by parliament, and the procedure to be followed.
At the continental level, the instrument of ratification or accession to the Protocol must be deposited by a government with the Chairperson of the Commission of the African Union. To that end, the African Union has embarked on sensitising Member States about the importance of signing, ratifying or acceding to the Maputo Protocol.
| AU Member State | DATE OF SIGNATURE | DATE OF RATIFICATION/ ACCESSION | DATE DEPOSITED | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algeria | 29 Dec 2003 | 20 Nov 2016 | 10 Jan 2017 | |
| Angola | 22 Jan 2007 | 30 Aug 2007 | 9 Nov 2007 | |
| Benin | 11 Feb 2004 | 30 Sep 2005 | 13 Oct 2005 | |
| Botswana | 13 Oct 2023 | 23 Oct 2023 | 1 Dec 2023 | |
| Burkina Faso | 26 Feb 2004 | 9 Jun 2006 | 9 Aug 2006 | |
| Burundi | 3 Dec 2003 | - | - | |
| Cameroon | 25 Jul 2006 | 13 Sep 2012 | 28 Dec 2012 | |
| Central African Republic | 17 Jun 2008 | 10 May 2012 | - | |
| Cape Verde | Unknown | 21 Jun 2005 | 22 Jul 2005 | |
| Chad | 6 Dec 2004 | - | - | |
| Côte d’Ivoire | 27 Feb 2004 | 5 Oct 2011 | 9 Mar 2012 | |
| Comoros | 26 Feb 2004 | 18 Mar 2004 | 16 Apr 2004 | |
| Congo | 27 Feb 2004 | 14 Dec 2011 | 6 Aug 2012 | |
| Djibouti | 18 Dec 2003 | 2 Feb 2005 | 4 Feb 2005 | |
| Democratic Rep. of Congo | 5 Dec 2003 | 9 Jun 2008 | 9 Feb 2009 | |
| Egypt | - | - | - | |
| Equatorial Guinea | 30 Jan 2005 | 27 Oct 2009 | 29 Jun 2011 | |
| Eritrea | 25 Apr 2012 | - | - | |
| Eswatini | 7 Dec 2004 | 5 Oct 2012 | 6 Nov 2012 | |
| Ethiopia | 1 Jun 2004 | 18 Jul 2018 | 17 Sep 2019 | |
| Gabon | 27 Jan 2005 | 10 Jan 2011 | 10 Feb 2011 | |
| Gambia | 11 Sep 2003 | 25 May 2005 | 6 Sep 2005 | |
| Ghana | 31 Oct 2003 | 13 Jun 2007 | 20 Jul 2007 | |
| Guinea-Bissau | 8 Mar 2005 | 19 Jun 2008 | 14 Oct 2008 | |
| Guinea | 16 Dec 2003 | 16 Apr 2012 | 17 Sep 2012 | |
| Kenya | 17 Dec 2003 | 6 Oct 2010 | 13 Oct 2010 | |
| Libya | 5 Nov 2003 | 23 May 2004 | 30 Jun 2004 | |
| Lesotho | 27 Feb 2004 | 26 Oct 2004 | 5 Nov 2004 | |
| Liberia | 16 Dec 2003 | 14 Dec 2007 | 15 Jul 2008 | |
| Madagascar | 28 Feb 2004 | - | - | |
| Mali | 9 Dec 2003 | 13 Jan 2005 | 3 Feb 2005 | |
| Malawi | Unknown | 20 May 2005 | 29 Jun 2005 | |
| Mauritania | - | 21 Sep 2005 | 14 Dec 2005 | |
| Mauritius | 29 Jan 2005 | 16 Jun 2017 | 23 Jun 2017 | |
| Morocco | - | - | - | |
| Mozambique | 15 Dec 2003 | 9 Dec 2005 | 30 Dec 2005 | |
| Namibia | 9 Dec 2003 | 11 Aug 2004 | 26 Aug 2004 | |
| Nigeria | 16 Dec 2003 | 16 Dec 2004 | 18 Feb 2005 | |
| Niger | 6 Jul 2004 | - | - | |
| Rwanda | 19 Dec 2003 | 25 Jun 2004 | 1 Jul 2004 | |
| South Africa | 16 Mar 2004 | 17 Dec 2004 | 14 Jan 2005 | |
| Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic | 20 Jun 2006 | 19 Mar 2022 | 27 May 2023 | |
| Senegal | 26 Dec 2003 | 27 Dec 2004 | 30 Jan 2005 | |
| Seychelles | 24 Jan 2006 | 9 Mar 2006 | 25 Apr 2006 | |
| Sierra Leone | 9 Dec 2003 | 3 Jul 2015 | 30 Oct 2015 | |
| Somalia | 23 Feb 2006 | - | - | |
| South Sudan | 24 Jan 2013 | 24 Feb 2023 | 7 Jun 2023 | |
| Sao Tome & Principe | 1 Feb 2010 | 18 Apr 2019 | 27 Jun 2019 | |
| Sudan | 30 Jun 2008 | - | - | |
| Tanzania | 5 Nov 2003 | 3 Mar 2007 | 7 May 2007 | |
| Togo | 30 Dec 2003 | 12 Oct 2005 | 26 Oct 2005 | |
| Tunisia | 30 Jan 2015 | 23 Aug 2018 | 27 Sep 2018 | |
| Uganda | 18 Dec 2003 | 22 Jul 2010 | 22 Jul 2010 | |
| Zambia | 3 Aug 2005 | 2 May 2006 | 7 Jun 2006 | |
| Zimbabwe | 18 Nov 2003 | 15 Apr 2008 | 5 Sep 2008 | |
